|
Pepper 3.7.0
A highly extensible plattform for conversion and
|
|
Pepper 3.7.0
A highly extensible plattform for conversion and
|
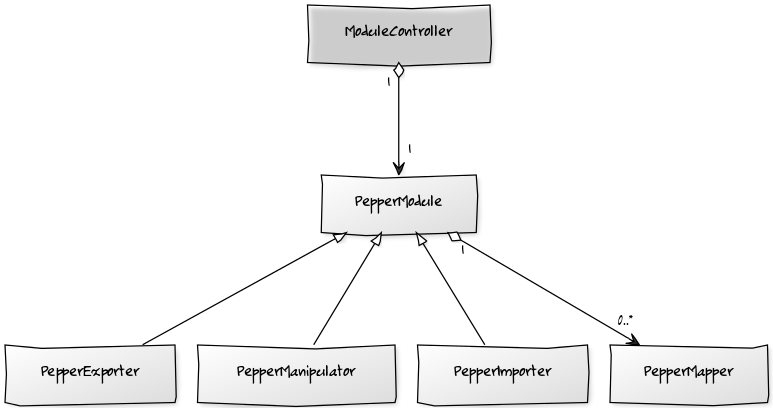
There is a specific interface for each type of module in Pepper. An importer must implement the interface org.corpus_tools.pepper.modules.PepperImporter, a manipulator must implement org.corpus_tools.pepper.modules.PepperManipulator and an exporter must implement org.corpus_tools.pepper.modules.PepperExporter. There is also a specific class to each module type implementing the corresponding interface:
Each module in your project must implements one of the interfaces and can extends one of these classes. The importer, manipulator and exporter classes implement the supertype org.corpus_tools.pepper.PepperModule and extend the class org.corpus_tools.pepper.impl.PepperModuleImpl. The following figure shows the inheritance model of Pepper modules and its connection to the Pepper framework.
A mapping process can be relatively time consuming, therefore the processing of documents is parallelized. This is possible since in Salt documents are independent from another. Each document is a partition and elements inside one documents have no references to the elements of another document. The parallelization in Java is realized via multi-threaded. Unfortunately in Java multi-threading is not that trivial and the easiest way to do is to separate each thread in an own class. Therefore a org.corpus_tools.pepper.modules.PepperModule object can instantiate an unbound number of org.corpus_tools.pepper.modules.PepperMapper objects. These objects contain the logic of a mapping and do the main work, while the rest regulates the workflow. Keep in mind, that when documents are partitions you must treat them as independent units and cannot assume the documents to come in a specific or fixed order. When you do not implement an importer, the order in which the documents reach your module depends on all the previous modules and is not deterministic.
The class org.corpus_tools.pepper.modules.ModuleController is a mediator between the concrete Pepper module and the Pepper framework. It initializes, starts and ends the modules processing.
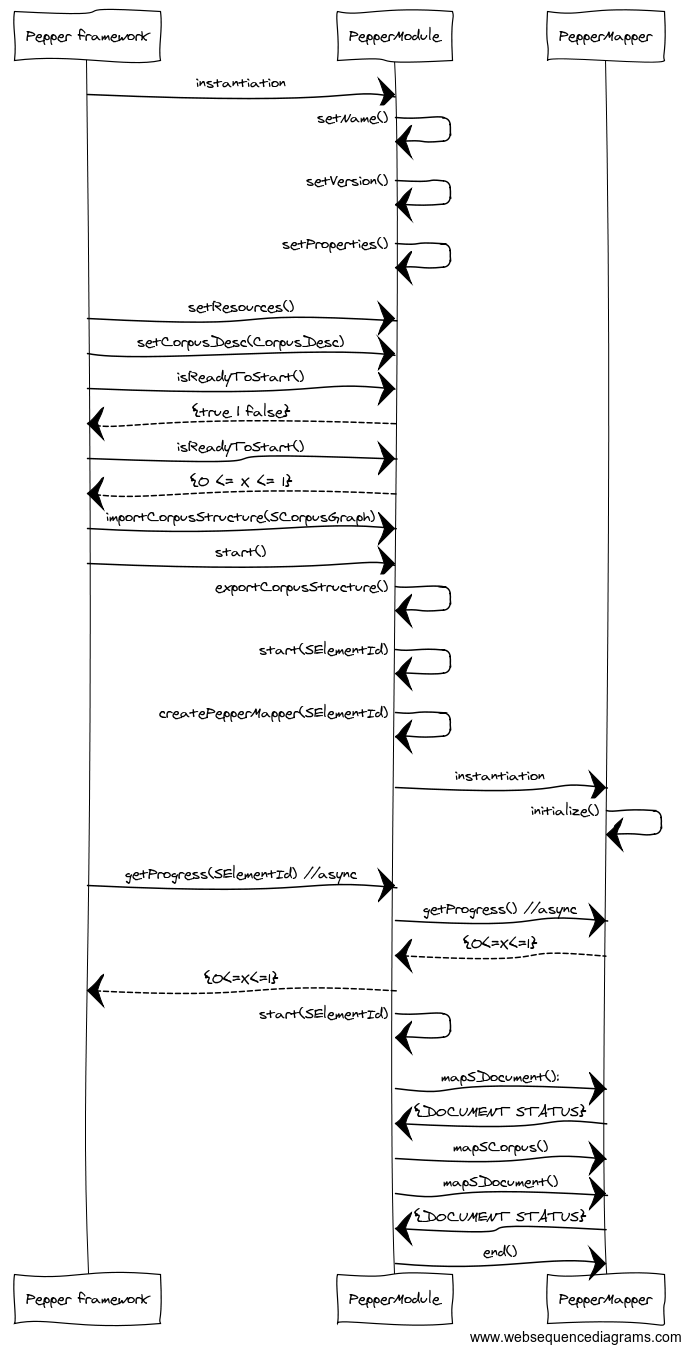
A mapping can be divided into several acts. Some of these acts correspond to the module's type, for instance a manipulator does not need to im- or export the corpus structure. Some of the acts are mandatory, some are recommended and some are optional, depending on your usecase. The following sections will explain the acts in detail.